
The most frequent serious adverse reactions reported in ≥2% of patients were pneumonia, pyrexia, diarrhea, pneumonitis, pleural effusion, dyspnea, acute kidney injury, infusion-related reaction, musculoskeletal pain, and pulmonary embolism.
#Checkmate 9la asco 2021 plus#
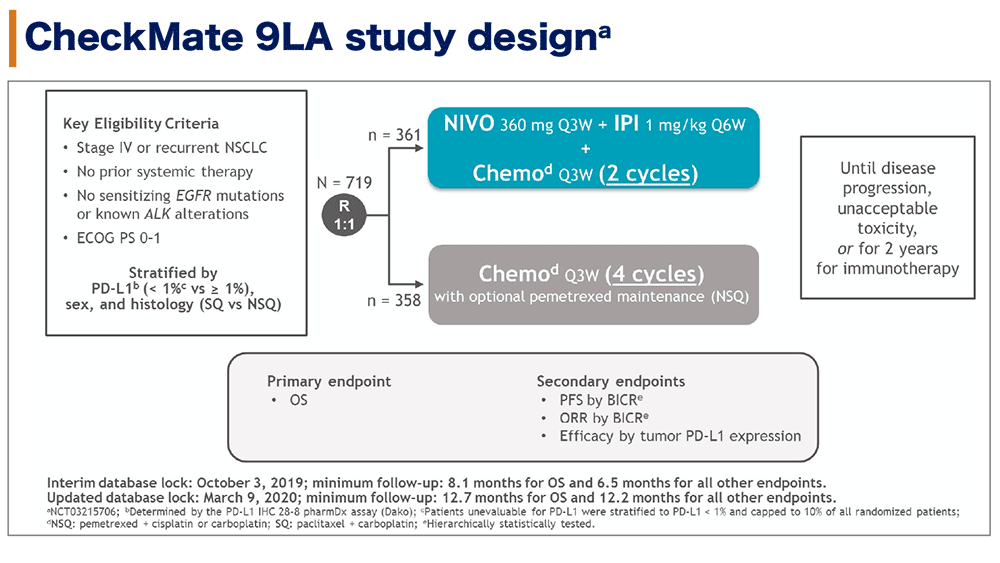
In Checkmate 743, serious adverse reactions occurred in 54% of patients receiving OPDIVO plus YERVOY. In Checkmate 057, fatal adverse reactions occurred these included events of infection (7 patients, including one case of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia), pulmonary embolism (4 patients), and limbic encephalitis (1 patient). The most frequent serious adverse reactions reported in ≥2% of patients receiving OPDIVO were pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, dyspnea, pyrexia, pleural effusion, pneumonitis, and respiratory failure. In Checkmate 017 and 057, serious adverse reactions occurred in 46% of patients receiving OPDIVO (n=418). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 7 (2%) patients, and included hepatic toxicity, acute renal failure, sepsis, pneumonitis, diarrhea with hypokalemia, and massive hemoptysis in the setting of thrombocytopenia. The most frequent (>2%) serious adverse reactions were pneumonia, diarrhea, febrile neutropenia, anemia, acute kidney injury, musculoskeletal pain, dyspnea, pneumonitis, and respiratory failure. In Checkmate 9LA, serious adverse reactions occurred in 57% of patients (n=358). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 1.7% of patients these included events of pneumonitis (4 patients), myocarditis, acute kidney injury, shock, hyperglycemia, multi-system organ failure, and renal failure. The most frequent (≥2%) serious adverse reactions were pneumonia, diarrhea/colitis, pneumonitis, hepatitis, pulmonary embolism, adrenal insufficiency, and hypophysitis. In Checkmate 227, serious adverse reactions occurred in 58% of patients (n=576). No fatal adverse reactions occurred in patients who received OPDIVO in combination with platinum-doublet chemotherapy. Dual immunotherapy-based combination resulted in clinical benefits across key subgroups of mNSCLC patients with high unmet need, including those with PD-L1 expression 2% included pneumonia and vomiting.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
